Amino acid cost and supply chain analysis for cultivated meat
This white paper explores amino acid costs and supply pathways for cultivated meat, drawing on industry data and value-chain expertise. It equips stakeholders to prioritize research and supply chain solutions critical for scaling a competitive cultivated meat industry.
Download summary & full report
How to make amino acids more affordable for cultivated meat
Unlocking a cost-effective amino acid supply is essential to scaling the cultivated meat industry. Amino acids represent a significant cost driver for cultivated meat production, due not only to the large quantities required, but also the complex supply chain needed to deliver them at the scale and suitability for food applications.
This white paper evaluates pathways to supply amino acids at the cost and volume required for a competitive cultivated meat industry.
This novel study combines future amino acid requirements, alternative sourcing strategies, and real-world price data to help stakeholders across the value chain prioritize the most impactful research and supply chain solutions as the cultivated meat industry scales.
Key findings
- The amino acid cost contribution to cultivated meat production could fall below $5/kg cultivated meat, representing a major improvement over previous estimates of approximately $18–$19/kg.
- Hydrolysates from raw materials hold long-term promise as cost-effective alternatives to amino acid fermentation. But their uptake is limited by technical challenges.
- The modeled price targets of $1.51–$11.27/kg for hydrolysates to compete with fermentation-derived amino acids are within reach.
- Batch-to-batch variability, solubility issues, and limited compositional data remain barriers to widespread adoption.
- High cost and supply-constrained amino acids present new innovation and sourcing opportunities.
- Six amino acids — serine, glutamine, asparagine, histidine, proline, and arginine — pose high risks to scaling cultivated meat due to cost, limited supply, and difficulty replacing them with alternatives.
- Strategic efforts to improve production efficiency, diversify sourcing, and stabilize prices of these high-impact inputs will be critical for long-term scalability.
Data highlights
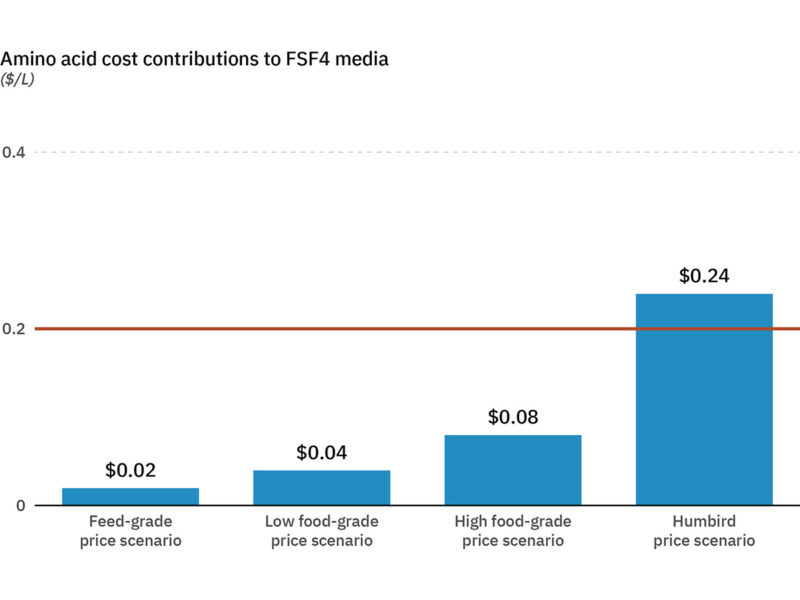
Figure 1. Total amino acid cost contributions to a commercial media across four price scenarios.
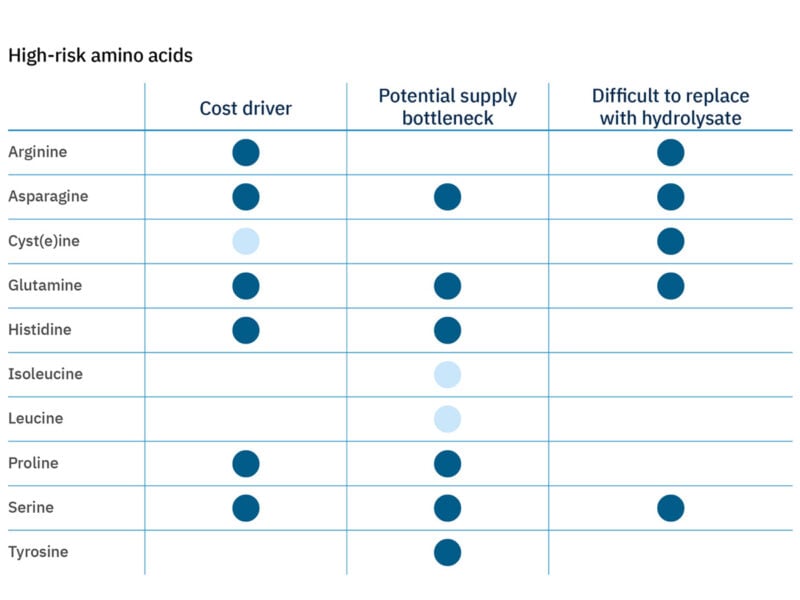
Figure 2. Heatmap showing high-risk amino acids from this analysis.
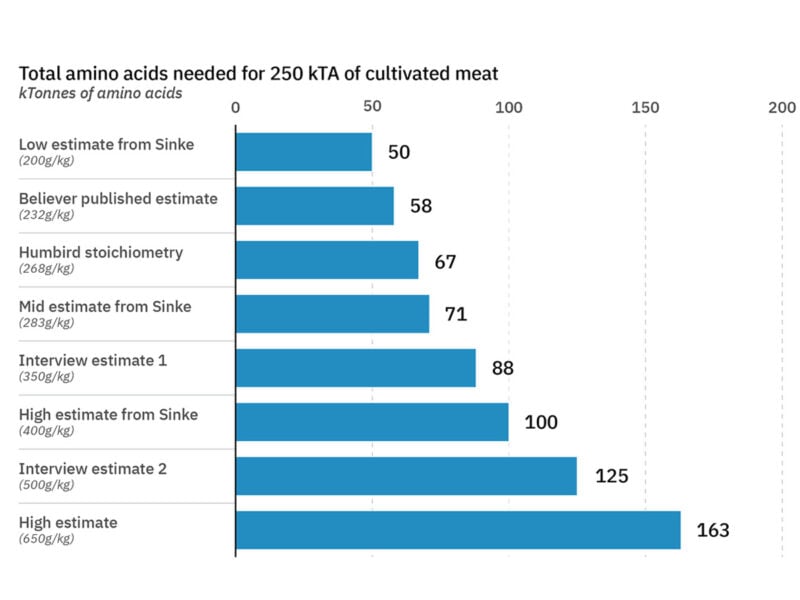
Figure 3. Projected total amino acid requirements to produce 250 kilotonnes of cultivated meat.
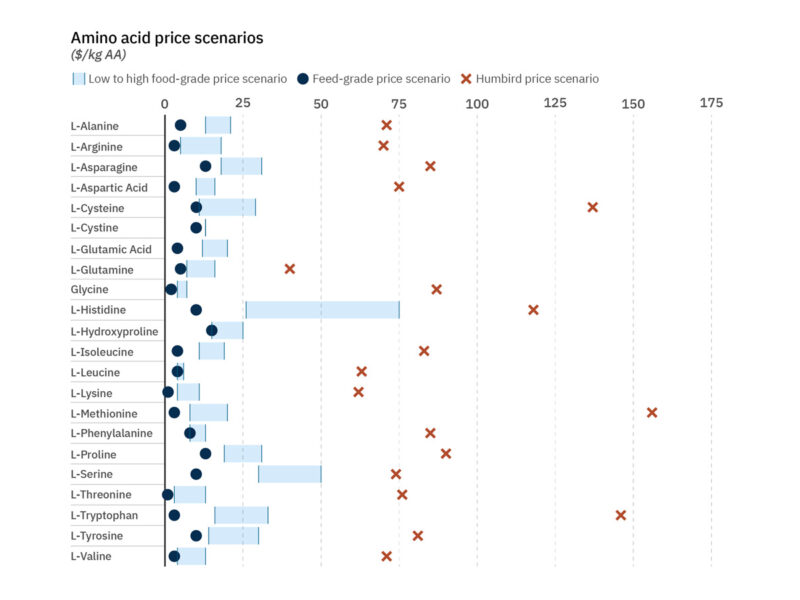
Figure 5. Amino acid price data (based on quotes and information obtained during interviews).
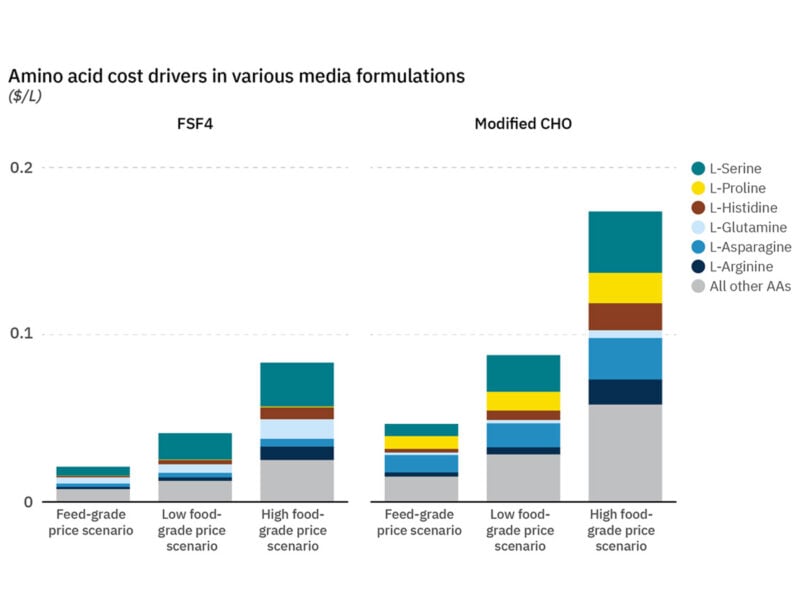
Figure 7. Individual amino acid cost drivers in FSF4 and modified CHO media based on multiple pricing scenarios.
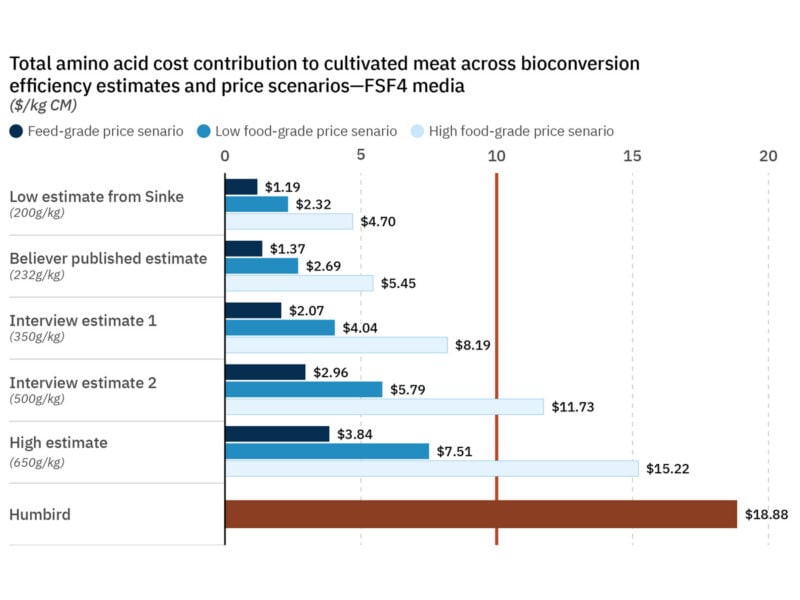
Figure 9a. Estimated costs of amino acids per kg of CM across multiple bioconversion efficiencies and pricing scenarios.
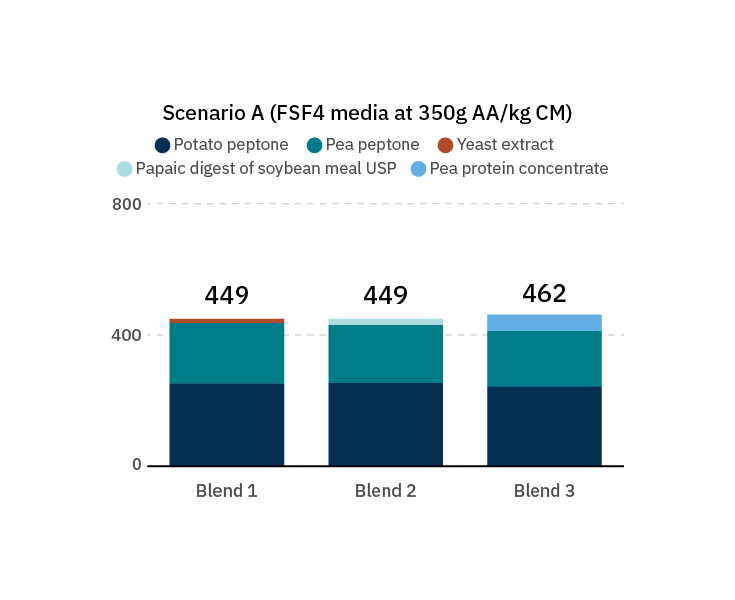
Figure 11. Top raw material or hydrolysate blends for one of four blending scenarios.

Watch our webinar
Experts Elliot Swartz and Marie Gibbons explore this novel analysis of amino acid scaling pathways for cultivated meat using real-world data and industry expertise. Learn how suppliers, CM producers, governments, and researchers can unlock the full potential of cultivated meat.
Download the report and data
Share your information to help us shape future content. We won’t contact you unless you opt in.
Downloads available:
- Full technical report
- Supporting data
- Interactive models for production volume, cost, hydrolysate blend optimization, and hydrolysate price targets

Resource
Give us feedback on our report
We want your input! Use this form to submit feedback, corrections, additional insights, data, and your thoughts on our report.
Related resources
Citation and DOI information
Gibbons, M., A. Bess, and E. Swartz. Amino acid cost and supply chain analysis for cultivated meat. Washington D.C.: Good Food Institute. 2025. https://doi.org/10.62468/xcjx6040





